常见的权限认证是通过提供“用户名密码”完成,业务中有一些 API,我们希望以 API
Token 的形式验证。例如 URL 上加上 token /api?token=xxxx 就允许API 的访问。这种设计背后的逻辑是用户名密码拥有较高的权限,而 API token 可以只给出某个子系统的权限,类似于 Github 的 Personal API
Tokens。
本文会介绍如何用 Spring Security 来实现。Spring Security 虽然功能强大,但配置起来经常让人云里雾里,所以我们要试图了解一些 Spring Security 的工作原理,再具体实现 API Token 的权限认证。
Spring Security 基本原理
Java Servlet 和 Spring Security 都使用了设计模式中的 责任链模式 。简单地说,它们都定义了许多过滤器(Filter),每一个请求都会经过层层过滤器的处理,最终返回。如下图:
其中,Spring Security 在 Servlet 的过滤链(filter chain)中注册了一个过滤器
FilterChainProxy,它会把请求代理到 Spring Security 自己维护的多个过滤链,每个过滤链会匹配一些 URL,如图中的 /foo/**,如果匹配则执行对应的过滤器。过滤链是有顺序的,一个请求只会执行第一条匹配的过滤链。Spring Security 的配置本质上就是新增、删除、修改过滤器。下图是配置了 http.formLogin() 的过滤链:
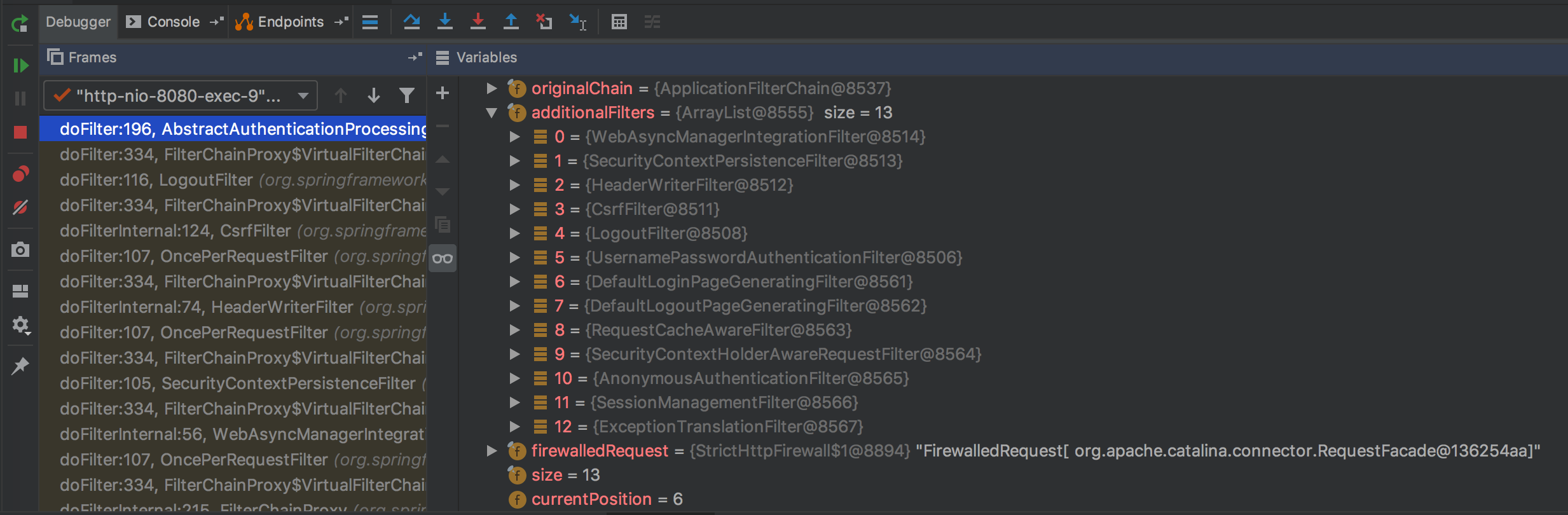
可以看到默认的过滤器里包含了许多内容,如 CsrfFilter 来生成和校验 CSRF Token
,UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 来处理用户名密码的认证,
SessionManagementFilter 来管理 Session 等等。而我们关心的“权限认证”,它其实分为两个部分:
- 认证(Authentication):即证明“你是你”,常见的如果用户名密码匹配,则认为操作者是该用户。
- 授权(Authorization):即判断“你有没有资格”,例如“删贴”功能只允许管理员使用。
认证(Authentication)
以用户名密码的方式为例,要认证一个用户是不是系统的用户,我们需要两个步骤:
- 一个从请求的报文中抽取用户名及密码信息等认证信息。认证信息需要实现
Authentication接口。 - 另一个用来验证认证信息是否正确,如密码是否正确、API token 是否正确。
- 额外地,判断该用户是否有资格访问某个 URL,这个属于授权。
验证用户、密码的逻辑一般需要自定义且常常会比较复杂,Spring Security 中的
AuthenticationManager 定义了验证的接口:
public interface AuthenticationManager { |
- 如果认证通过,返回认证信息(比如擦除密码后的认证信息)
- 如果认证失败,抛
AuthenticationException异常。 - 如果无法决定,返回 null。
Spring Security 内部使用最多的实现是 ProviderManager,而它内部又使用了一个认证的链条,包含了多个AuthenticationProvier,ProviderManager 会逐一调用它们直到有一个 provider成功返回。
public interface AuthenticationProvider { |
与 AuthenticationManager 不同的是它多了一个 supports 方法用来判断Provider
是否支持当前的认证信息。如一个 API Token 的认证器就不支持用户名密码的认证信息。
另外,ProviderManager 还定义了父子关系,如果当前 ProviderManager 中所有的 Provier 都无法认证某个信息,它就会让父 ProviderManager 来判断。如图:
理论上我们不需要理解这些内容,完全可以自己编写一个过滤器来处理所有需求。只是如果使用了这套接口,就能享受 Spring Security 的一些“基础设施”,例如抛
AuthenticationException 时,ExceptionTranslationFilter 会调用配置好的
authenticationEntryPoint.commence() 方法进行处理,返回 401 等等。
授权(Authorization)
要判断“你有没有资格”,首先要知道关于“你”的信息,也就是前一小节中说的
Authentication 接口;其次需要知道要访问的资源及资源的配置,如要访问 URL,该
URL 能被什么角色访问。类似地,Spring Security 已经定义了相关的接口,授权会在
FilterSecurityInterceptor 中启动。
public interface AccessDecisionManager { |
函数 decide 会决定授权是否成功,如果权限不足则抛 AccessDeniedException 异常。函数参数说明:
authentication代表了“认证信息”,从中可以获得诸如当前用户的角色等信息object即要访问的资源,如某个 URL 或是某个函数configAttributes代表该资源的配置,如该 URL 只能被“管理员”角色(ROLE_ADMIN)访问。
Spring Security 中,具体的授权策略是“投票机制”,每一个 AccessDecisionVoter
都能投票,而最后如何统计结果,由 AccessDecisionManager 的具体实现决定。如
AffirmativeBased 只需要有人赞成即可;ConsensusBased 需要多数人赞成;
UnanimousBased 需要所有人赞成。默认使用 AffirmativeBased。
同 Authentication 一样,遵循这套逻辑,Spring Security 的默认配置就能减少我们的工作量。例如上面提到的投票机制,还有抛 AccessDeniedException 异常时返回 403 等处理。
配置
Spring Security 的运行原理不难理解,但如何达到想要的配置一直是我学习时的痛点。这里也只是简要说明,具体的配置不是三言两语能说清的。下面举一个简单的示例,说明一些对应关系:
|
- 继承
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter开始。之前提到 Spring Security 可以包含多条过滤链,每个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter对应一条过滤链。③ 中指定要匹配的 URL 模式,顺序由@Order指定。 - 重载
configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth)方法来配置认证逻辑,一份WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter配置会生成一个ProviderManager,而这个configure方法可以提供多个AuthenticationProvier。 - 指定当前过滤链要匹配的 URL 模式。用
antMatcher指定一个模式,使用requestMatcher或requestMatchers来进行高级配置,如指定多个模式。 - 通过
addFilter相关方法可以在当前过滤链中添加过滤器,但似乎没有删除的方法。 hasRole等用来指定“授权”的逻辑,比如该行表示访问所有的 URL 都需要API角色。
API Token 实现
要实现开头说的 API Token 的权限认证,我们需要下面几样东西:
- 一个
Authentication的实现,用于存放 token 相关的认证信息。 - 一个过滤器,抽取请求中的 token 信息
- 一个
AuthenticationProvier用来确认 token 认证信息是否正确。 - 当认证失败时,我们想返回自定义的错误信息,因此需要一个过滤器。
认证信息
由于 API token 只需要存放 token 本身即可,所以实现如下:
public class TokenAuthentication implements Authentication { |
抽取 token 的过滤器
因为 token 信息是在 URL 中指定的,所以这个过滤器会读取 URL 中的 parameter 并生成上节定义的 TokenAuthentication:
public class TokenAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { // ① |
- ① 中继承自
OncePerRequestFilter没有特别用意,它的功能是能防止这个过滤器被调用多次 - ② 处获取 URL 中的 token 并把生成的 Authentication 存放在 SecurityContext 里,供后续逻辑使用
- ③ 中设置过 attribute 后,该过滤器不会被再被调用
- ④ 中执行后面的过滤器
校验逻辑
上面会 URL 中获得 Token,我们需要与数据库中的 token 比较看是否一致,这里就用内存中的比较代替:
public class TokenAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider { |
错误处理
我们希望在错误时,返回 200 状态码,同时 body 中包含 "success": false及具体的错误信息。
public class ResultExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean { |
组装配置
具体的配置和上面提到的差不多,注意到我们还关闭了 CSRF 和 Session。
|
完整的代码可以在 Spring Security Example 找到。
小结
每次用 Spring Security 都是现搜现用,如果示例不工作时往往不知道如何处理,所以这些更深入地学习了原理并做了笔记,希望各位看官用得上。
- Spring Security 会注册 FilterChainProxy,自身包含多个 Filter Chain
- 认证 Authentication 与授权 Authorization 是分开的两套逻辑
AuthenticationManager包含多个AuthenticationProvider且可以有父节点- 授权的入口是
AccessDecisionManager,它的几个实现类代表着不同的投票方法。 - 每个继承
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的类定义一条新的 Filter Chain
最后我们用了上面的知识实现了基于 API token 的认证,授权仍旧用的 Spring Security 默认的机制。
参考
- https://spring.io/guides/topicals/spring-security-architecture/ Spring Security 官方架构文档,本文的知识很多来源于此
- Spring Security源码分析一:Spring Security认证过程 详细认证过程分析,对于理解认证链路很有帮助。
- Spring Security源码分析二:Spring Security授权过程